
Singapore, officially titled the Republic of Singapore, is an autonomous island nation and city-state situated in maritime Southeast Asia. Its geographical domain encompasses a primary island alongside 63 satellite islands and islets, as well as an outlying islet.
Functioning as a parliamentary republic with a Westminster system, Singapore operates under a unicameral parliamentary government and adheres to a legal system grounded in common law. Its economic framework is distinguished by a highly evolved market economy, historically rooted in extensive re-export.
Labor Code
Government approval is generally not required for foreigners to establish business in Singapore and 100% foreign ownership is permitted. There is an exception for banks and other financial institutions, which require approval from the Monetary Authority of Singapore, and must obtain certain special licenses.
An in-country bank account is not mandatory to make global payroll payments to employees or authorities in Singapore. An office address is a minimal requirement by law if you plan to register the following:
- Branch office (must appoint at least two local agents which will act on your organization’s behalf)
- Incorporated company
- Representative office
- Subsidiary
Global payroll in Singapore is regulated by law and there are no payroll taxes. Employers in Singapore are responsible for submitting income tax returns and paying social taxes for employees.
Minimum Wage
Singapore does not have a minimum wage for most sectors. Wages are determined by market demand and the supply of labor.
Working Hours
The standard workday is eight hours, while the standard workweek is 44 hours.
Overtime Pay
For employees covered by the Employment Act, overtime pay is 150% of the hourly basic pay rate. A "13th month payment" is optional.
Employees
The Employment Act of Singapore (Chapter 91) is the principal statute that regulates the employer/employee relationship. It expresses the terms and conditions for the employees covered by the Act.
Singapore has two categories of employees:
- Employees who are covered under the Employment Act (covers most employees in the service of an employer).
- Employees who are not covered under the Employment Act (include seafarers, domestic workers, civil servants, and statutory board employees).
Taxes
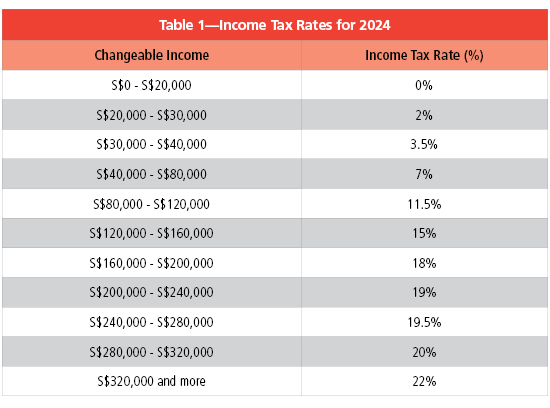
Singapore follows a progressive resident tax rate starting at 0% and ending at 22% above S$320,000. There is no capital gains or inheritance tax. Individuals are taxed only on the income earned in Singapore. The income earned by individuals while working overseas is not subject to taxation barring a few exceptions.
Income tax rates depend on an individual's tax residency status. You will be treated as a tax resident for a particular year of assessment (YA) if you are the following:
- A Singapore citizen or Permanent Resident who resides in Singapore except for temporary absences; or
- A foreigner who has stayed/worked in Singapore either:
- For at least 183 days in the previous calendar year; or
- Continuously for three consecutive years, even if the period of stay in Singapore may be less than 183 days in the first year and/or third year; or
- A foreigner who has worked in Singapore for a continuous period straddling two calendar years and the total period of stay is at least 183 days. This applies to employees who entered Singapore but excludes directors of a company, public entertainers, and professionals.
If you do not meet the conditions stated above, you will be treated as a nonresident of Singapore for tax purposes.
Singapore’s personal income tax rates for resident taxpayers are progressive. This means higher income earners pay a proportionately higher tax, with the current highest personal income tax rate at 22%.
As of 2024, the income tax rate for nonresident individuals (except on employment income and certain income taxable at reduced withholding rates) will be raised from 22% to 24%. This is to maintain parity between the income tax rate of nonresident individuals and the top marginal income tax rate of resident individuals.
Income Tax Rates
Starting in the 2024 tax year, the top marginal personal income tax rate will be increased for Singapore tax residents with income of more than S$500,000 per year. Chargeable income from S$500,000 up to S$1 million will be taxable at a rate of 23%; income more than S$1 million will be subject to a tax rate of 24% (see Table 1).
Social Insurance, Contributions
Only Singaporean citizens and permanent residents are required to contribute to the Central Provident Fund (CPF) which is the national pension scheme. Expatriates are not required to make social security contributions.
Employees are required to contribute 20% and employers are required to contribute 17% of ordinary monthly wages to social security.
Payroll Tax
Employers are required to contribute 17% of monthly wages into Singapore’s social security scheme, the CPF.
Corporate Tax
The corporate income tax rate is 17% on chargeable income.
Value Added Tax
The goods and services tax (GST) rate is 9% as of 1 January 2024.
Dividends
The following dividends are subject to income tax:
- Dividends paid by cooperatives;
- Foreign-sourced dividends derived by individuals through a partnership in Singapore (such dividends may qualify for tax exemption if certain conditions are met);
- Income distribution from Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) derived by individuals through a partnership in Singapore, or from the carrying on of a trade, business, or profession in REITs.
How Withholding Works
There are no withholding obligations in Singapore for employers; however, contributions to social security schemes, the Skill Development Levy (SDL), and the Foreign Workers Levy (FWL) are required.
Domestic corporations paying certain types of income to nonresidents are required to withhold tax. Unless a lower treaty rate applies, interest on loans and rentals from movable property are subject to withholding tax at the rate of 15%. Royalty payments are subject to withholding at the rate of 10%.
Returns, Tax Credits
The Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) will automatically refund tax credits and pay interest on tax credits not refunded within 30 days from the date the tax credit arises, unless it is a situation where an automatic tax refund will not be made.
Tax credits are refunded via GIRO, PayNow (individual income tax, GST, and corporate income tax only), telegraphic transfer, or cheque.
Time Off
Employees are entitled to various types of leave in Singapore, including the following:
- Annual Leave—If you've been with your employer for at least three months, you're entitled to paid annual leave. The number of days you receive depends on your length of service.
- Maternity Leave—Working mothers can take either 16 weeks of government-paid maternity leave (GPML) or 12 weeks of maternity leave, depending on various criteria including the citizenship of the child.
- Paternity Leave—Eligible working fathers, including those who are self-employed, can take two weeks of paid paternity leave, funded by the government.
- Sick Leave—After three months of employment, employees are entitled to paid outpatient sick leave and paid hospitalization leave.
National Holidays
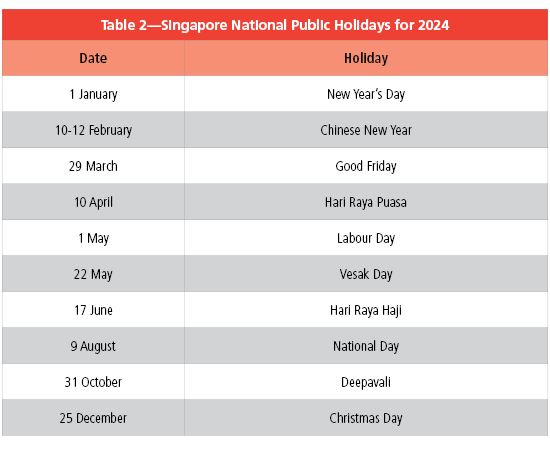
There are 10 Singapore public holidays in 2024 (see Table 2).
Foreign Hires
Foreign employees are entitled to the same rights as Singaporean citizens and are generally covered by the same tax and workplace laws.
Visas
Different types of visas exist for foreign workers depending on skill level. The following are the types of visas employees may apply for when working abroad in Singapore:
- Employment Pass (EP)
- Entrepreneur Pass (EntrePass)
- Personalized Employment Pass (PEP)
- Work Permit
- S Pass
- Miscellaneous Work Pass
Taxes
Nonresident individuals are taxed at a flat rate of 24%, except that employment income is taxed at a flat rate of 15% or at resident rates with personal reliefs, whichever yields a higher tax.
Culture
Even though Singapore is small, it boasts a rich diversity of languages, religions, and cultures. The preservation of racial and religious harmony is deemed integral to Singapore's achievements and has contributed significantly to the cultivation of a distinct Singaporean identity.